Lung Abscess
Introduction
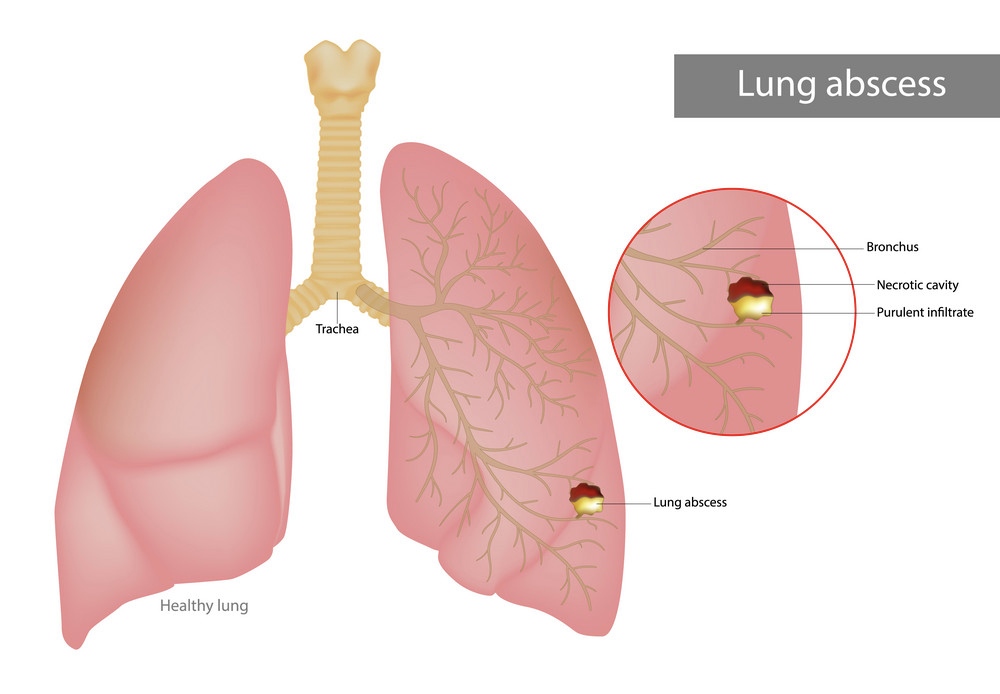
A lung abscess is a rare but serious medical condition characterized by a localized collection of pus and infected material within the lung tissue. It is typically a complication of an underlying respiratory infection, aspiration (inhaling a foreign substance into the lungs), or an impaired immune system. Lung abscesses can vary in size and severity, and prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent potentially life-threatening complications.
Causes
1. Bacterial infections: The most common cause of lung abscesses is bacterial infections, particularly those caused by anaerobic bacteria. These include Streptococcus species, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Bacteroides species.
2. Aspiration: Inhaling or aspirating substances such as food particles, vomit, or foreign objects into the lungs can lead to the development of a lung abscess. This can occur during episodes of impaired consciousness, after excessive alcohol consumption, or in individuals with swallowing disorders.
3. Impaired immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplant recipients, or those with HIV/AIDS, are at increased risk of developing lung abscesses due to their reduced ability to fight off infections.
4. Spread from other infections: In some cases, lung abscesses can develop as a result of the spread of infection from other parts of the body, such as a pre-existing chest infection or a bloodstream infection (sepsis).
5. Bronchial obstruction: Blockages or obstructions in the airways, such as those caused by lung cancer or foreign objects, can increase the risk of developing a lung abscess by allowing the accumulation of infected material.
Risk Factors
1. Underlying respiratory conditions: Individuals with pre-existing lung conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiectasis, or cystic fibrosis, are at higher risk of developing lung abscesses due to the impaired ability to clear respiratory secretions.
2. Poor oral hygiene: Poor dental health and oral hygiene can increase the risk of aspirating bacteria from the mouth into the lungs, leading to the development of a lung abscess.
3. Alcohol abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption can impair the gag reflex and increase the risk of aspiration, which can lead to a lung abscess.
4. Neurological disorders: Conditions that affect swallowing or increase the risk of aspiration, such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, or dementia, can increase the likelihood of developing a lung abscess.
5. Immunocompromised state: Individuals with weakened immune systems due to conditions like HIV/AIDS, cancer, or immunosuppressive medications are at higher risk of developing lung abscesses.
Symptoms
1. Cough: A persistent and productive cough, often producing foul-smelling or blood-tinged sputum, is a common symptom of a lung abscess.
2. Fever and chills: High fevers, accompanied by chills or night sweats, are frequently associated with lung abscesses due to the body’s inflammatory response to the infection.
3. Chest pain: Localized chest pain or discomfort may be experienced, especially when breathing deeply or coughing.
4. Shortness of breath: As the lung abscess grows, it can cause difficulty breathing or a feeling of shortness of breath.
5. Fatigue and weakness: The body’s efforts to fight the infection can lead to feelings of extreme tiredness and weakness.
6. Weight loss: Unintentional weight loss may occur due to the increased energy demands of the body’s immune response and the reduced appetite associated with the illness.
Complications
1. Respiratory failure: If left untreated, a lung abscess can continue to grow and potentially lead to respiratory failure, a life-threatening condition where the lungs are unable to provide sufficient oxygen to the body.
2. Sepsis: The infection causing the lung abscess can spread to the bloodstream, leading to sepsis, a potentially fatal systemic inflammatory response.
3. Empyema: Pus from the lung abscess can accumulate in the space between the lung and the chest wall, a condition known as empyema, which can further impair breathing and require surgical drainage.
4. Bronchopleural fistula: In some cases, a lung abscess can erode through the chest wall, creating an abnormal connection (fistula) between the bronchial tubes and the pleural space, leading to air leakage and potential pneumothorax (collapsed lung).
5. Hemoptysis: Coughing up blood (hemoptysis) can occur if the lung abscess erodes into a blood vessel within the lung.
Differential Diagnosis
Lung abscesses share symptoms with other respiratory conditions, and it is important to differentiate them from these conditions to provide appropriate treatment. The differential diagnosis for lung abscesses may include:
1. Pneumonia: Both lung abscesses and pneumonia can cause cough, fever, and respiratory distress, but pneumonia typically involves a larger area of the lung and may not form a localized collection of pus.
2. Lung cancer: Certain types of lung cancer, particularly those that cause obstructive lesions, can mimic the symptoms of a lung abscess, such as cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath.
3. Bronchiectasis: This chronic condition, characterized by abnormally dilated and damaged bronchial tubes, can increase the risk of lung infections and the formation of lung abscesses.
4. Tuberculosis: In some cases, tuberculosis (TB) can present with localized lung lesions that may resemble lung abscesses, especially in patients with weakened immune systems.
5. Fungal infections: Fungal infections, such as aspergillosis or mucormycosis, can cause localized lung lesions and abscesses, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
Preventions
1. Prompt treatment of respiratory infections: Seeking early medical attention and promptly treating respiratory infections can help prevent the development of lung abscesses.
2. Good oral hygiene: Maintaining good oral health and practicing proper dental hygiene can reduce the risk of aspirating bacteria from the mouth into the lungs.
3. Avoiding risk factors: Limiting alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and managing underlying medical conditions that increase the risk of aspiration can help prevent lung abscesses.
4. Vaccination: Receiving recommended vaccinations, such as the pneumococcal vaccine and influenza vaccine, can help prevent respiratory infections that may lead to lung abscesses.
5. Proper airway management: For individuals at risk of aspiration, such as those with swallowing disorders or certain neurological conditions, proper airway management and precautions may be necessary to prevent the development of lung abscesses.
Diagnosis
1. Medical history and physical examination: The healthcare provider will take a detailed medical history, including symptoms, risk factors, and any underlying conditions. A physical examination will be performed, with a focus on assessing respiratory function and identifying any abnormal lung sounds.
2. Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray is often the initial diagnostic tool used to detect the presence of a lung abscess, which may appear as a localized area of opacity or fluid collection within the lung.
3. Computed tomography (CT) scan: A CT scan of the chest can provide more detailed images of the lung abscess, including its size, location, and any associated complications, such as empyema or fistula formation.
4. Sputum culture: A sample of the patient’s sputum (phlegm or mucus coughed up from the lungs) may be collected and cultured to identify the specific bacteria or microorganisms causing the infection.
5. Blood tests: Blood tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) and inflammatory markers (e.g., C-reactive protein), can help assess the presence and severity of the infection.
6. Bronchoscopy: In some cases, a bronchoscopy (a procedure where a flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the bronchial tubes) may be performed to directly visualize the lung abscess and collect samples for further analysis.
Treatments
1. Antibiotics: Intravenous (IV) antibiotics are the primary treatment for lung abscesses. The choice of antibiotic will depend on the specific bacteria or microorganisms identified through sputum or blood cultures, as well as the severity of the infection. Antibiotic therapy may be required for several weeks to ensure complete resolution of the abscess.
2. Drainage procedures: In some cases, interventional procedures may be necessary to drain the pus and infected material from the lung abscess. This can be done through percutaneous drainage, where a needle or catheter is inserted into the abscess under imaging guidance, or through surgical drainage techniques.
3. Bronchoscopic intervention: For lung abscesses that are accessible through the bronchial tubes, a bronchoscope may be used to remove debris or pus from the abscess cavity.
4. Surgical resection: In rare and severe cases, surgical removal (resection) of the affected portion of the lung may be required if the lung abscess is large, fails to respond to other treatments, or causes significant complications.
5. Supportive care: Supportive measures, such as oxygen therapy, pain management, and nutritional support, may be necessary to help manage symptoms and aid in the recovery process.
6. Treatment of underlying conditions: Addressing and treating any underlying medical conditions, such as respiratory disorders, immunodeficiencies, or swallowing disorders, is crucial to prevent the recurrence of lung abscesses.
Important Key Points
- A lung abscess is a localized collection of pus and infected material within the lung tissue.
- Common causes include bacterial infections, aspiration of substances, impaired immune system, and spread from other infections.
- Risk factors include underlying respiratory conditions, poor oral hygiene, alcohol/substance abuse, neurological disorders, and immunocompromised state.
- Symptoms include persistent cough with foul-smelling sputum, fever, chills, chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and weight loss.
- Complications can be severe, including respiratory failure, sepsis, empyema, bronchopleural fistula, and hemoptysis.
- Differential diagnosis includes pneumonia, lung cancer, bronchiectasis, tuberculosis, and fungal infections.
- Prevention involves prompt treatment of respiratory infections, good oral hygiene, avoiding risk factors, vaccination, and proper airway management.
- Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, chest X-ray, CT scan, sputum culture, blood tests, and sometimes bronchoscopy.
- Treatment typically involves intravenous antibiotics, drainage procedures (percutaneous or surgical), bronchoscopic intervention, surgical resection in severe cases, and supportive care.
- Addressing underlying conditions is crucial to prevent recurrence.
- Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to prevent life-threatening complications and promote recovery.
Note: This is a general overview, and it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized medical advice and treatment.
