Bronchiectasis
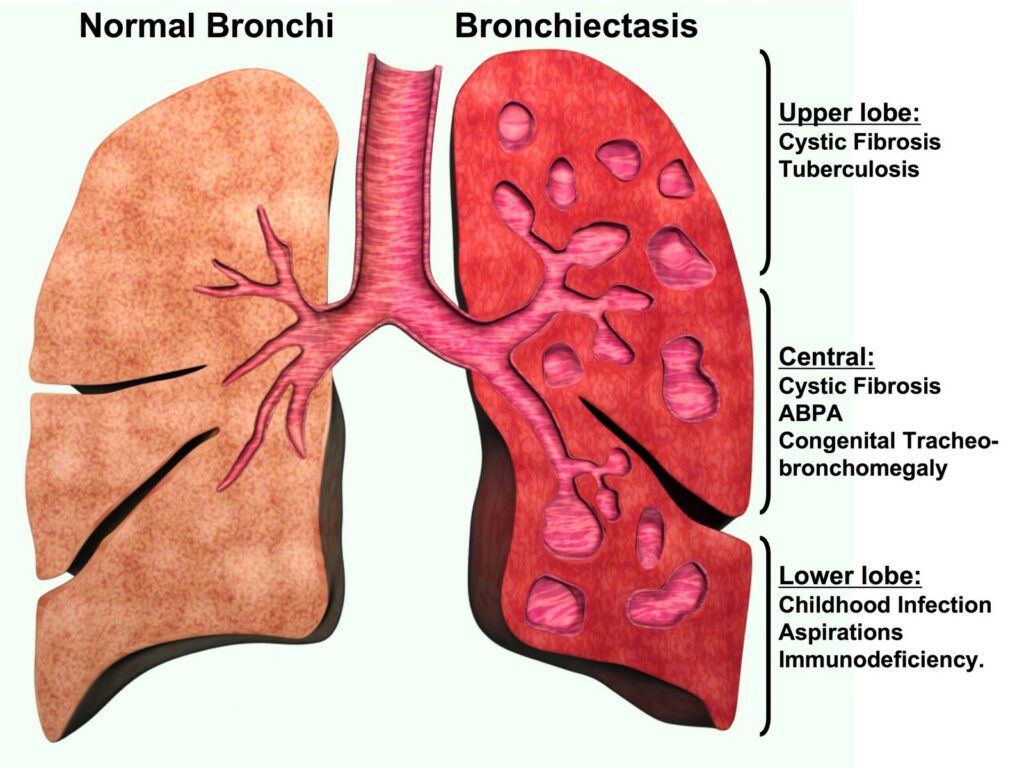
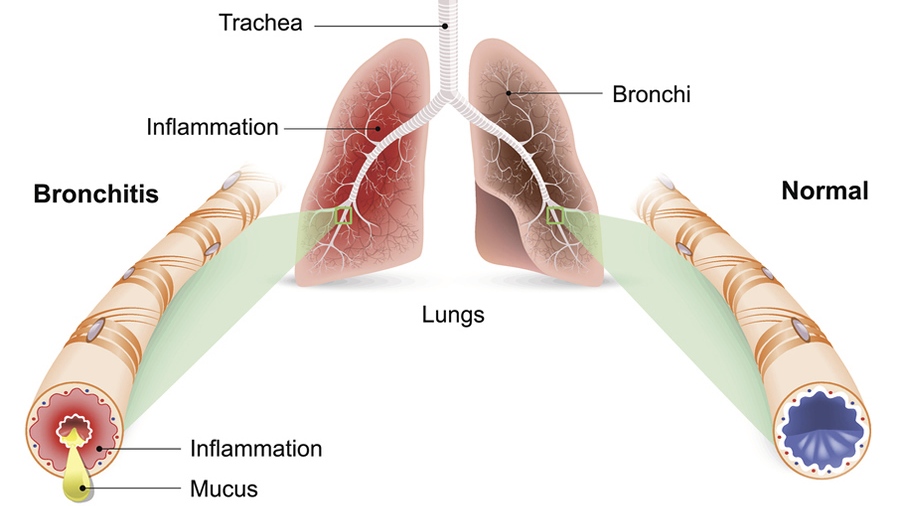
Bronchiectasis Introduction Bronchiectasis is a chronic respiratory condition characterized by abnormal and permanent dilation (widening) of the bronchial tubes (airways) in the lungs. This dilation is typically caused by damage or destruction of the bronchial walls, leading to the accumulation of mucus and bacteria, which can further damage the airways and perpetuate the condition. Causes […]